Update (Dec 2023)
The Node SDK is now called the JavaScript SDK since version 4.0. The new version not only works on Node.js, but also in the browser, Deno, Bun, Cloudflare Workers, and more.
We're thrilled to release version 2.0 of the AssemblyAI Node SDK. The SDK has been rewritten from scratch using TypeScript and provides easy-to-use access to our API. You can use the SDK from Node.js (or a compatible framework) and enjoy an intuitive SDK with typed documentation whether you're using JavaScript or TypeScript.
Here are 3 samples of how you can use the new SDK.
1. Transcribe an audio or video file:
import { AssemblyAI } from "assemblyai";
const client = new AssemblyAI({
apiKey: process.env.ASSEMBLYAI_API_KEY,
})
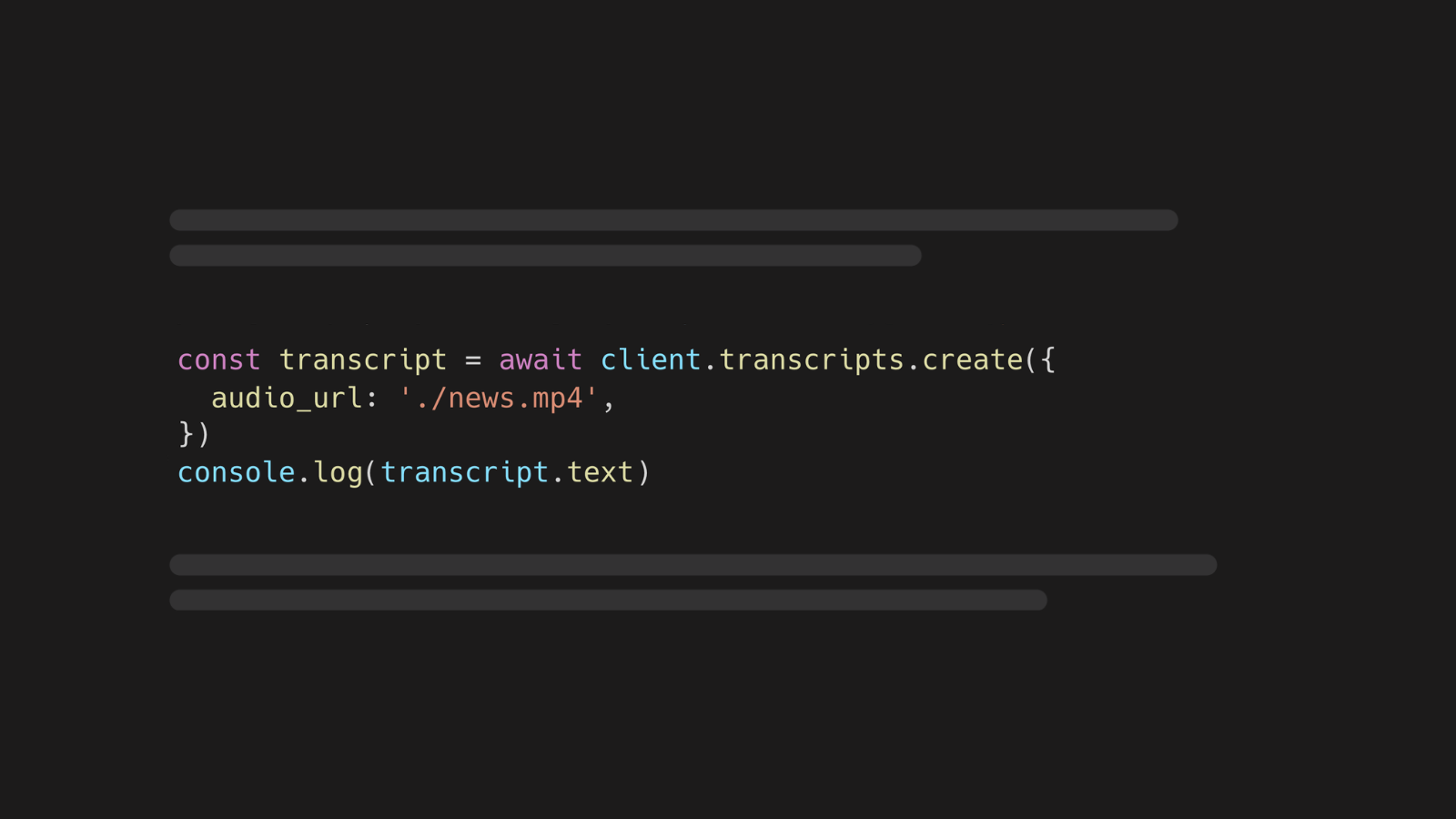
const transcript = await client.transcripts.create({
audio_url: './news.mp4',
})
console.log(transcript.text)
Learn how to transcribe audio by following this step-by-step guide.
2. Talk to your audio data using LeMUR:
const { response } = await client.lemur.questionAnswer({
transcript_ids: [transcript.id],
questions: [
{
question: 'What are the highlights of the newscast?',
answer_format: 'text',
}
]
})
console.log(response[0].question, response[0].answer)
With just a few lines of code, you can quickly transcribe your audio asynchronously and use LLMs on top of your spoken audio data using LeMUR.
3. Transcribe audio in real-time:
const rt = client.realtime.createService();
rt.on("transcript", (transcript: TranscriptMessage) => console.log('Transcript:', transcript));
rt.on("error", (error: Error) => console.error('Error', error));
rt.on("close", (code: number, reason: string) => console.log('Closed', code, reason));
await rt.connect();
// Pseudo code for getting audio from a microphone for example
getAudio((chunk) => {
rt.sendAudio(chunk);
});
await rt.close();
Learn how to transcribe audio in real-time coming from a microphone by following this step-by-step guide.
To learn more about the SDK, check out the GitHub repository README and the AssemblyAI documentation.